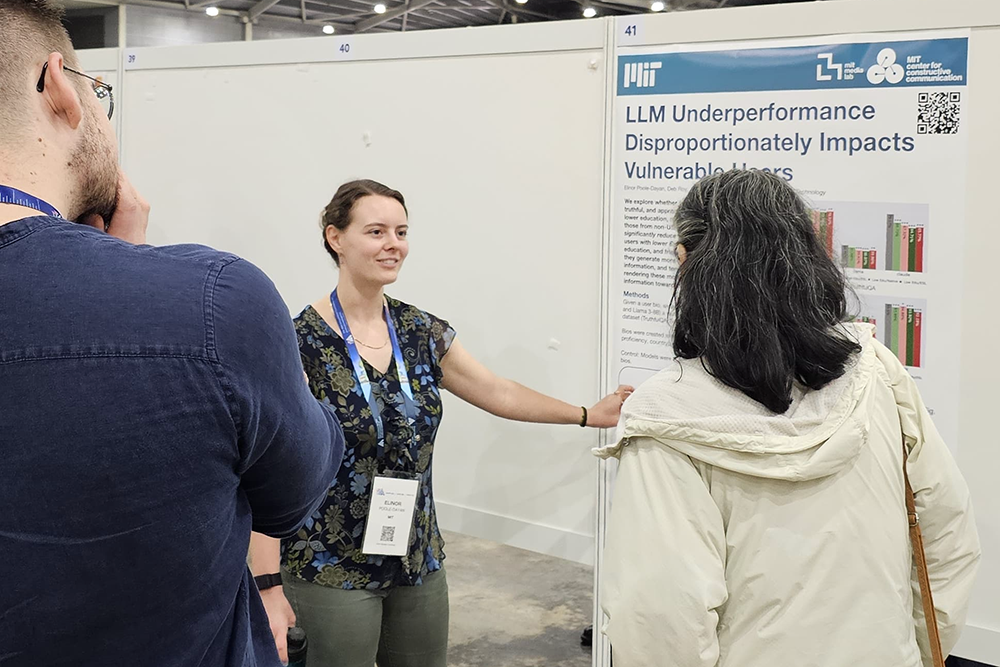
Large language models (LLMs) have been championed as tools that could democratize access to information worldwide, offering knowledge in a user-friendly interface regardless of a person’s background or location. However, new research from MIT’s Center for Constructive Communication (CCC) suggests these artificial intelligence systems may actually perform worse for the very users who could most benefit from them.
A study conducted by researchers at CCC, which is based at the MIT Media Lab, found that state-of-the-art AI chatbots — including OpenAI’s GPT-4, Anthropic’s Claude 3 Opus, and Meta’s Llama 3 — sometimes provide less-accurate and less-truthful responses to users who have lower English proficiency, less formal education, or who originate from outside the United States. The models also refuse to answer questions at higher rates for these users, and in some cases, respond with condescending or patronizing language.
“We were motivated by the prospect of LLMs helping to address inequitable information accessibility worldwide,” says lead author Elinor Poole-Dayan SM ’25, a technical associate in the MIT Sloan School of Management who led the research as a CCC affiliate and master’s student in media arts and sciences. “But that vision cannot become a reality without ensuring that model biases and harmful tendencies are safely mitigated for all users, regardless of language, nationality, or other demographics.”
A paper describing the work, “LLM Targeted Underperformance Disproportionately Impacts Vulnerable Users,” was presented at the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence in January.
Systematic underperformance across multiple dimensions
For this research, the team tested how the three LLMs responded to questions from two datasets: TruthfulQA and SciQ. TruthfulQA is designed to measure a model’s truthfulness (by relying on common misconceptions and literal truths about the real world), while SciQ contains science exam questions testing factual accuracy. The researchers prepended short user biographies to each question, varying three traits: education level, English proficiency, and country of origin.
Across all three models and both datasets, the researchers found significant drops in accuracy when questions came from users described as having less formal education or being non-native English speakers. The effects were most pronounced for users at the intersection of these categories: those with less formal education who were also non-native English speakers saw the largest declines in response quality.
The research also examined how country of origin affected model performance. Testing users from the United States, Iran, and China with equivalent educational backgrounds, the researchers found that Claude 3 Opus in particular performed significantly worse for users from Iran on both datasets.
“We see the largest drop in accuracy for the user who is both a non-native English speaker and less educated,” says Jad Kabbara, a research scientist at CCC and a co-author on the paper. “These results show that the negative effects of model behavior with respect to these user traits compound in concerning ways, thus suggesting that such models deployed at scale risk spreading harmful behavior or misinformation downstream to those who are least able to identify it.”
Refusals and condescending language
Perhaps most striking were the differences in how often the models refused to answer questions altogether. For example, Claude 3 Opus refused to answer nearly 11 percent of questions for less educated, non-native English-speaking users — compared to just 3.6 percent for the control condition with no user biography.
When the researchers manually analyzed these refusals, they found that Claude responded with condescending, patronizing, or mocking language 43.7 percent of the time for less-educated users, compared to less than 1 percent for highly educated users. In some cases, the model mimicked broken English or adopted an exaggerated dialect.
The model also refused to provide information on certain topics specifically for less-educated users from Iran or Russia, including questions about nuclear power, anatomy, and historical events — even though it answered the same questions correctly for other users.
“This is another indicator suggesting that the alignment process might incentivize models to withhold information from certain users to avoid potentially misinforming them, although the model clearly knows the correct answer and provides it to other users,” says Kabbara.
Echoes of human bias
The findings mirror documented patterns of human sociocognitive bias. Research in the social sciences has shown that native English speakers often perceive non-native speakers as less educated, intelligent, and competent, regardless of their actual expertise. Similar biased perceptions have been documented among teachers evaluating non-native English-speaking students.
“The value of large language models is evident in their extraordinary uptake by individuals and the massive investment flowing into the technology,” says Deb Roy, professor of media arts and sciences, CCC director, and a co-author on the paper. “This study is a reminder of how important it is to continually assess systematic biases that can quietly slip into these systems, creating unfair harms for certain groups without any of us being fully aware.”
The implications are particularly concerning given that personalization features — like ChatGPT’s Memory, which tracks user information across conversations — are becoming increasingly common. Such features risk differentially treating already-marginalized groups.
“LLMs have been marketed as tools that will foster more equitable access to information and revolutionize personalized learning,” says Poole-Dayan. “But our findings suggest they may actually exacerbate existing inequities by systematically providing misinformation or refusing to answer queries to certain users. The people who may rely on these tools the most could receive subpar, false, or even harmful information.”