What is an AI Agent?
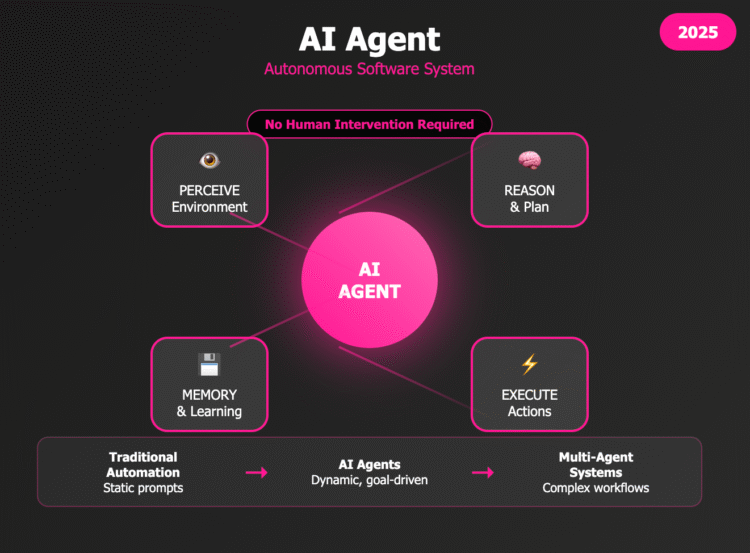
An AI Agent is an autonomous software system that can perceive its environment, interpret data, reason, and execute actions to achieve specific goals without explicit human intervention. Unlike traditional automation, AI agents integrate decision-making, learning, memory, and multi-step planning capabilities—making them suitable for complex real-world tasks. In essence, an AI agent acts as a cognitive layer atop data and tools, intelligently navigating, transforming, or responding to situations in real time.
Why AI Agents Matter in 2025
AI agents are now at the forefront of next-generation software architecture. As businesses look to integrate generative AI into workflows, AI agents enable modular, extensible, and autonomous decision systems. With multi-agent systems, real-time memory, tool execution, and planning capabilities, agents are revolutionizing industries from DevOps to education. The shift from static prompts to dynamic, goal-driven agents is as significant as the leap from static websites to interactive web applications.
Types of AI Agents
1. Simple Reflex Agents
These agents operate based on the current percept, ignoring the rest of the percept history. They function using condition-action rules (if-then statements). For example, a thermostat responds to temperature changes without storing previous data.
2. Model-Based Reflex Agents
These agents enhance reflex behavior by maintaining an internal state that depends on the percept history. The state captures information about the world, helping the agent handle partially observable environments.
3. Goal-Based Agents
Goal-based agents evaluate future actions to achieve a desired state or goal. By simulating different possibilities, they can select the most efficient path to meet specific objectives. Planning and search algorithms are fundamental here.
4. Utility-Based Agents
These agents not only pursue goals but also consider the desirability of outcomes by maximizing a utility function. They are essential in scenarios requiring trade-offs or probabilistic reasoning (e.g., economic decision-making).
5. Learning Agents
Learning agents continuously improve their performance by learning from experience. They consist of four main components: a learning element, a performance element, a critic (to provide feedback), and a problem generator (to suggest exploratory actions).
6. Multi-Agent Systems (MAS)
These systems involve multiple AI agents interacting in a shared environment. Each agent may have different goals, and they may cooperate or compete. MAS is useful in robotics, distributed problem-solving, and simulations.
7. Agentic LLMs
Emerging in 2024–2025, these are advanced agents powered by large language models. They incorporate capabilities such as reasoning, planning, memory, and tool use. Examples include AutoGPT, LangChain Agents, and CrewAI.
Key Components of an AI Agent
1. Perception (Input Interface)
The perception module enables the agent to observe and interpret its environment. It processes raw inputs such as text, audio, sensor data, or visual feeds and translates them into internal representations for reasoning.
2. Memory (Short-Term and Long-Term)
Memory allows agents to store and retrieve past interactions, actions, and observations. Short-term memory supports context retention within a session, while long-term memory can persist across sessions to build user or task profiles. Often implemented using vector databases.
3. Planning and Decision-Making
This component enables agents to define a sequence of actions to achieve a goal. It uses planning algorithms (e.g., Tree-of-Thoughts, graph search, reinforcement learning) and can evaluate multiple strategies based on goals or utilities.
4. Tool Use and Action Execution
Agents interact with APIs, scripts, databases, or other software tools to act in the world. The execution layer handles these interactions securely and effectively, including function calls, shell commands, or web navigation.
5. Reasoning and Control Logic
Reasoning frameworks manage how an agent interprets observations and decides on actions. This includes logic chains, prompt engineering techniques (e.g., ReAct, CoT), and routing logic between modules.
6. Feedback and Learning Loop
Agents assess the success of their actions and update their internal state or behavior. This may involve user feedback, task outcome evaluation, or self-reflective strategies to improve over time.
7. User Interface
For human-agent interaction, a user interface—like a chatbot, voice assistant, or dashboard—facilitates communication and feedback. It bridges natural language understanding and action interfaces.
Leading AI Agent Frameworks in 2025
• LangChain
A dominant open-source framework for constructing LLM-based agents using chains, prompts, tool integration, and memory. It supports integrations with OpenAI, Anthropic, FAISS, Weaviate, web scraping tools, Python/JS execution, and more.
• Microsoft AutoGen
A framework geared toward multi-agent orchestration and code automation. It defines distinct agent roles—Planner, Developer, Reviewer—that communicate via natural language, enabling collaborative workflows.
• Semantic Kernel
An enterprise-grade toolkit from Microsoft that embeds AI into apps using “skills” and planners. It is model-agnostic, supports enterprise languages (Python, C#), and seamlessly integrates with LLMs like OpenAI and Hugging Face.
• OpenAI Agents SDK (Swarm)
A lightweight SDK defining agents, tools, handoffs, and guardrails. Optimized for GPT-4 and function-calling, it enables structured workflows with built-in monitoring and traceability.
• SuperAGI
A comprehensive agent-operating system offering persistent multi-agent execution, memory handling, visual runtime interface, and a marketplace for plug-and-play components.
• CrewAI
Focused on team-style orchestration, CrewAI allows developers to define specialized agent roles (e.g., Planner, Coder, Critic) and coordinate them in pipelines. It integrates seamlessly with LangChain and emphasizes collaboration.
• IBM watsonx Orchestrate
A no-code, enterprise SaaS solution for orchestrating “digital worker” agents across business workflows with drag-and-drop simplicity.
Practical Use Cases for AI Agents 🌐
🔹 Enterprise IT & Service Desk Automation
AI agents streamline internal support workflows—routing helpdesk tickets, diagnosing issues, and resolving common problems automatically. For instance, agents like IBM’s AskIT reduce IT support calls by 70%, while Atomicwork’s Diagnostics Agent supports self-service troubleshooting directly within teams’ chat tools.
🔹 Customer-Facing Support & Sales Assistance
These agents handle high-volume inquiries—from order tracking to product recommendations— by integrating with CRMs and knowledge bases. They boost user experience and deflect routine tickets. Case in point: e-commerce chatbots that manage returns, process refunds, and reduce support costs by ~65%. Botpress-powered sales agents have even increased lead volume by ~50%.
🔹 Contract & Document Analysis (Legal & Finance)
AI agents can analyze, extract, and summarize data from contracts and financial documents—reducing time spent by up to 75%. This supports sectors like banking, insurance, and legal where rapid, reliable insight is crucial.
🔹 E‑commerce & Inventory Optimization
Agents predict demand, track inventory, and handle returns or refunds with minimal human oversight. Walmart-style AI assistants and image-based product search (e.g., Pinterest Lens) enhance personalized shopping experiences and conversion rates.
🔹 Logistics & Operational Efficiency
In logistics, AI agents optimize delivery routes and manage supply chains. For example, UPS reportedly saved $300 million annually using AI-driven route optimization. In manufacturing, agents monitor equipment health via sensor data to predict and preempt breakdowns.
🔹 HR, Finance & Back‑Office Workflow Automation
AI agents automate internal tasks—from processing vacation requests to payroll queries. IBM’s digital HR agents automate 94% of routine queries, significantly reducing HR workload. Agents also streamline invoice processing, financial reconciliation, and compliance checks using document intelligence techniques.
🔹 Research, Knowledge Management & Analytics
AI agents support research by summarizing reports, retrieving relevant insights, and generating dashboards. Google Cloud’s generative AI agents can transform large datasets and documents into conversational insights for analysts.
AI Agent vs. Chatbot vs. LLM
| Feature | Chatbot | LLM | AI Agent |
|---|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Task-specific dialogue | Text generation | Goal-oriented autonomy |
| Tool Use | No | Limited | Extensive (APIs, code, search) |
| Memory | Stateless | Short-term | Stateful + persistent |
| Adaptability | Predefined | Moderately adaptive | Fully adaptive with feedback loop |
| Autonomy | Reactive | Assistive | Autonomous + interactive |
The Future of Agentic AI Systems
The trajectory is clear: AI agents will become modular infrastructure layers across enterprise, consumer, and scientific domains. With advancements in:
- Planning Algorithms (e.g., Graph-of-Thoughts, PRM-based planning)
- Multi-Agent Coordination
- Self-correction and Evaluation Agents
- Persistent Memory Storage and Querying
- Tool Security Sandboxing and Role Guardrails
…we expect AI agents to mature into co-pilot systems that blend decision-making, autonomy, and accountability.
FAQs About AI Agents
Q: Are AI agents just LLMs with prompts?
A: No. True AI agents orchestrate memory, reasoning, planning, tool use, and adaptiveness beyond static prompts.
Q: Where can I build my first AI agent?
A: Try LangChain templates, Autogen Studio, or SuperAgent—all designed to simplify agent creation.
Q: Do AI agents work offline?
A: Most rely on cloud-based LLM APIs, but local models (e.g., Mistral, LLaMA, Phi) can run agents offline.
Q: How are AI agents evaluated?
A: Emerging benchmarks include AARBench (task execution), AgentEval (tool use), and HELM (holistic evaluation).
Conclusion
AI Agents represent a major evolution in AI system design—moving from passive generative models to proactive, adaptive, and intelligent agents that can interface with the world. Whether you’re automating DevOps, personalizing education, or building intelligent assistants, the agentic paradigm offers scalable and explainable intelligence.