During early development, tissues and organs begin to bloom through the shifting, splitting, and growing of many thousands of cells.
A team of MIT engineers has now developed a way to predict, minute by minute, how individual cells will fold, divide, and rearrange during a fruit fly’s earliest stage of growth. The new method may one day be applied to predict the development of more complex tissues, organs, and organisms. It could also help scientists identify cell patterns that correspond to early-onset diseases, such as asthma and cancer.
In a study appearing today in the journal Nature Methods, the team presents a new deep-learning model that learns, then predicts, how certain geometric properties of individual cells will change as a fruit fly develops. The model records and tracks properties such as a cell’s position, and whether it is touching a neighboring cell at a given moment.
The team applied the model to videos of developing fruit fly embryos, each of which starts as a cluster of about 5,000 cells. They found the model could predict, with 90 percent accuracy, how each of the 5,000 cells would fold, shift, and rearrange, minute by minute, during the first hour of development, as the embryo morphs from a smooth, uniform shape into more defined structures and features.
“This very initial phase is known as gastrulation, which takes place over roughly one hour, when individual cells are rearranging on a time scale of minutes,” says study author Ming Guo, associate professor of mechanical engineering at MIT. “By accurately modeling this early period, we can start to uncover how local cell interactions give rise to global tissues and organisms.”
The researchers hope to apply the model to predict the cell-by-cell development in other species, such zebrafish and mice. Then, they can begin to identify patterns that are common across species. The team also envisions that the method could be used to discern early patterns of disease, such as in asthma. Lung tissue in people with asthma looks markedly different from healthy lung tissue. How asthma-prone tissue initially develops is an unknown process that the team’s new method could potentially reveal.
“Asthmatic tissues show different cell dynamics when imaged live,” says co-author and MIT graduate student Haiqian Yang. “We envision that our model could capture these subtle dynamical differences and provide a more comprehensive representation of tissue behavior, potentially improving diagnostics or drug-screening assays.”
The study’s co-authors are Markus Buehler, the McAfee Professor of Engineering in MIT’s Department of Civil and Environmental Engineering; George Roy and Tomer Stern of the University of Michigan; and Anh Nguyen and Dapeng Bi of Northeastern University.
Points and foams
Scientists typically model how an embryo develops in one of two ways: as a point cloud, where each point represents an individual cell as point that moves over time; or as a “foam,” which represents individual cells as bubbles that shift and slide against each other, similar to the bubbles in shaving foam.
Rather than choose between the two approaches, Guo and Yang embraced both.
“There’s a debate about whether to model as a point cloud or a foam,” Yang says. “But both of them are essentially different ways of modeling the same underlying graph, which is an elegant way to represent living tissues. By combining these as one graph, we can highlight more structural information, like how cells are connected to each other as they rearrange over time.”
At the heart of the new model is a “dual-graph” structure that represents a developing embryo as both moving points and bubbles. Through this dual representation, the researchers hoped to capture more detailed geometric properties of individual cells, such as the location of a cell’s nucleus, whether a cell is touching a neighboring cell, and whether it is folding or dividing at a given moment in time.
As a proof of principle, the team trained the new model to “learn” how individual cells change over time during fruit fly gastrulation.
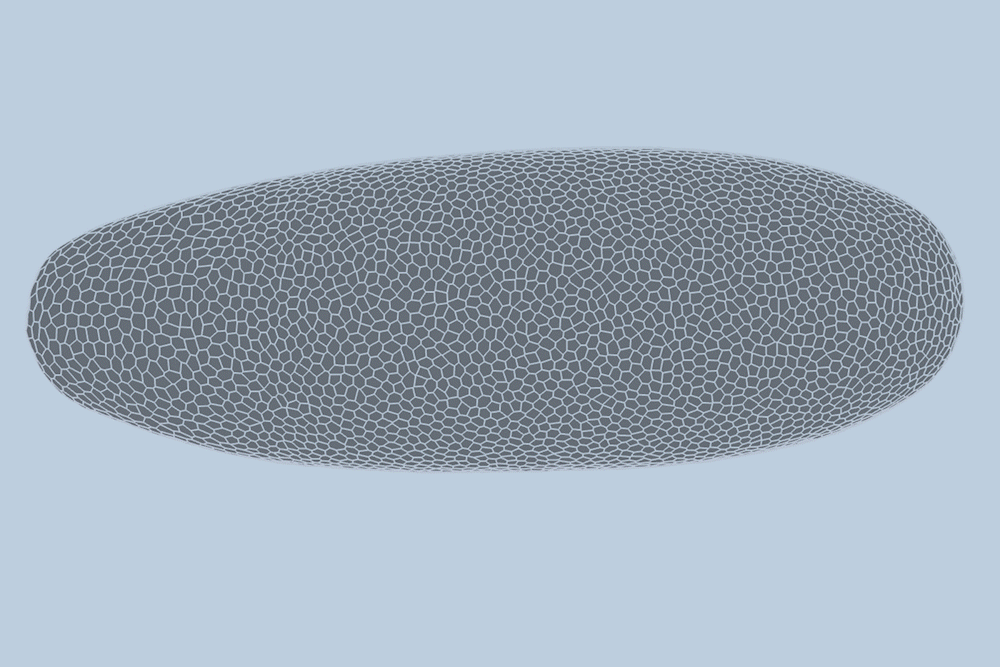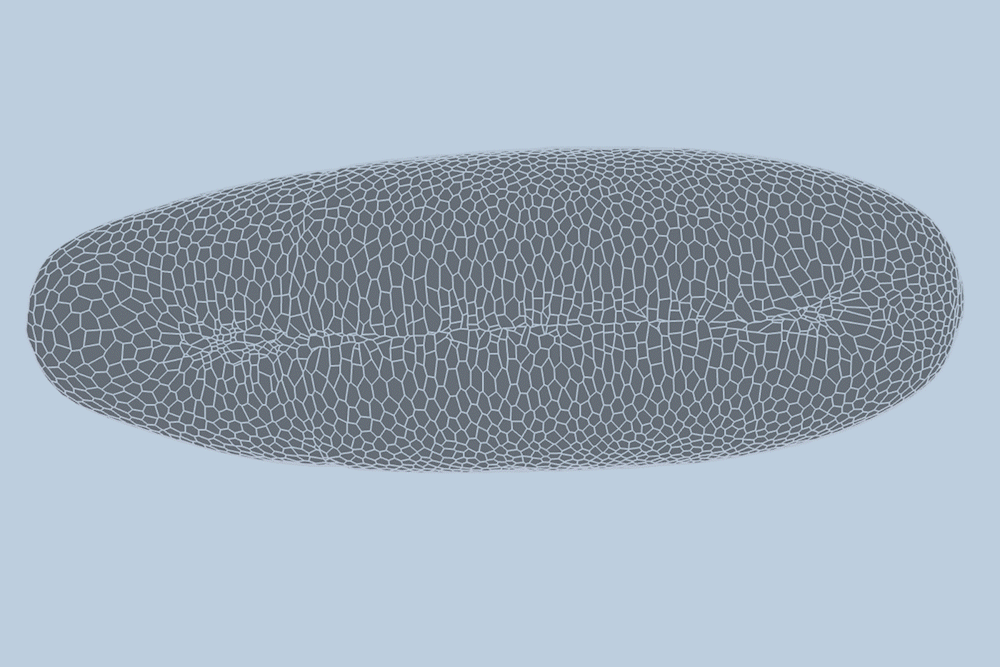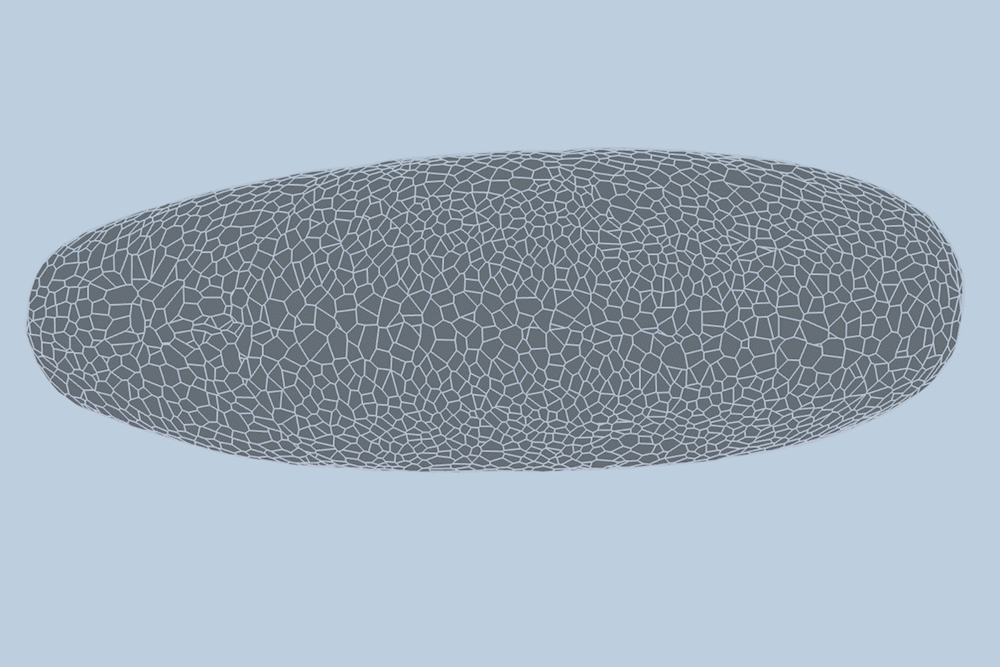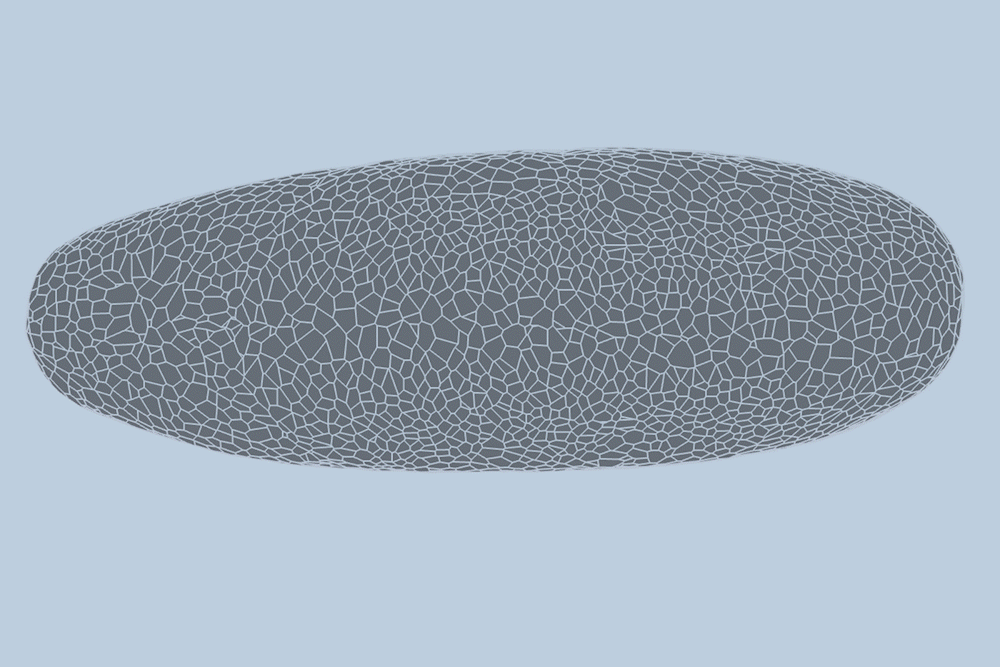
“The overall shape of the fruit fly at this stage is roughly an ellipsoid, but there are gigantic dynamics going on at the surface during gastrulation,” Guo says. “It goes from entirely smooth to forming a number of folds at different angles. And we want to predict all of those dynamics, moment to moment, and cell by cell.”
Where and when
For their new study, the researchers applied the new model to high-quality videos of fruit fly gastrulation taken by their collaborators at the University of Michigan. The videos are one-hour recordings of developing fruit flies, taken at single-cell resolution. What’s more, the videos contain labels of individual cells’ edges and nuclei — data that are incredibly detailed and difficult to come by.
“These videos are of extremely high quality,” Yang says. “This data is very rare, where you get submicron resolution of the whole 3D volume at a pretty fast frame rate.”
The team trained the new model with data from three of four fruit fly embryo videos, such that the model might “learn” how individual cells interact and change as an embryo develops. They then tested the model on an entirely new fruit fly video, and found that it was able to predict with high accuracy how most of the embryo’s 5,000 cells changed from minute to minute.
Specifically, the model could predict properties of individual cells, such as whether they will fold, divide, or continue sharing an edge with a neighboring cell, with about 90 percent accuracy.
“We end up predicting not only whether these things will happen, but also when,” Guo says. “For instance, will this cell detach from this cell seven minutes from now, or eight? We can tell when that will happen.”
The team believes that, in principle, the new model, and the dual-graph approach, should be able to predict the cell-by-cell development of other multiceullar systems, such as more complex species, and even some human tissues and organs. The limiting factor is the availability of high-quality video data.
“From the model perspective, I think it’s ready,” Guo says. “The real bottleneck is the data. If we have good quality data of specific tissues, the model could be directly applied to predict the development of many more structures.”
This work is supported, in part, by the U.S. National Institutes of Health.