In this tutorial, we explore the power of self-supervised learning using the Lightly AI framework. We begin by building a SimCLR model to learn meaningful image representations without labels, then generate and visualize embeddings using UMAP and t-SNE. We then dive into coreset selection techniques to curate data intelligently, simulate an active learning workflow, and finally assess the benefits of transfer learning through a linear probe evaluation. Throughout this hands-on guide, we work step by step in Google Colab, training, visualizing, and comparing coreset-based and random sampling to understand how self-supervised learning can significantly improve data efficiency and model performance. Check out the FULL CODES here.
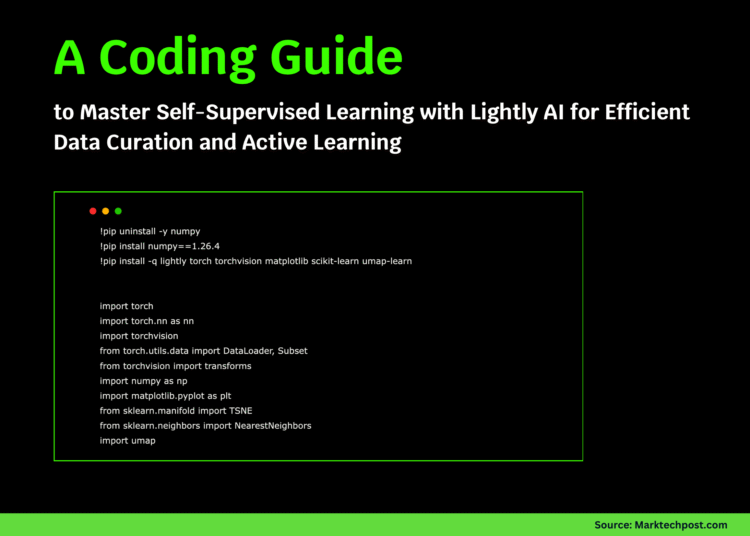
!pip uninstall -y numpy
!pip install numpy==1.26.4
!pip install -q lightly torch torchvision matplotlib scikit-learn umap-learn
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
import torchvision
from torch.utils.data import DataLoader, Subset
from torchvision import transforms
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from sklearn.manifold import TSNE
from sklearn.neighbors import NearestNeighbors
import umap
from lightly.loss import NTXentLoss
from lightly.models.modules import SimCLRProjectionHead
from lightly.transforms import SimCLRTransform
from lightly.data import LightlyDataset
print(f"PyTorch version: {torch.__version__}")
print(f"CUDA available: {torch.cuda.is_available()}")We begin by setting up the environment, ensuring compatibility by fixing the NumPy version and installing essential libraries like Lightly, PyTorch, and UMAP. We then import all necessary modules for building, training, and visualizing our self-supervised learning model, confirming that PyTorch and CUDA are ready for GPU acceleration. Check out the FULL CODES here.
class SimCLRModel(nn.Module):
"""SimCLR model with ResNet backbone"""
def __init__(self, backbone, hidden_dim=512, out_dim=128):
super().__init__()
self.backbone = backbone
self.backbone.fc = nn.Identity()
self.projection_head = SimCLRProjectionHead(
input_dim=512, hidden_dim=hidden_dim, output_dim=out_dim
)
def forward(self, x):
features = self.backbone(x).flatten(start_dim=1)
z = self.projection_head(features)
return z
def extract_features(self, x):
"""Extract backbone features without projection"""
with torch.no_grad():
return self.backbone(x).flatten(start_dim=1)We define our SimCLRModel, which uses a ResNet backbone to learn visual representations without labels. We remove the classification head and add a projection head to map features into a contrastive embedding space. The model’s extract_features method allows us to obtain raw feature embeddings directly from the backbone for downstream analysis. Check out the FULL CODES here.
def load_dataset(train=True):
"""Load CIFAR-10 dataset"""
ssl_transform = SimCLRTransform(input_size=32, cj_prob=0.8)
eval_transform = transforms.Compose([
transforms.ToTensor(),
transforms.Normalize((0.4914, 0.4822, 0.4465), (0.2023, 0.1994, 0.2010))
])
base_dataset = torchvision.datasets.CIFAR10(
root="./data", train=train, download=True
)
class SSLDataset(torch.utils.data.Dataset):
def __init__(self, dataset, transform):
self.dataset = dataset
self.transform = transform
def __len__(self):
return len(self.dataset)
def __getitem__(self, idx):
img, label = self.dataset[idx]
return self.transform(img), label
ssl_dataset = SSLDataset(base_dataset, ssl_transform)
eval_dataset = torchvision.datasets.CIFAR10(
root="./data", train=train, download=True, transform=eval_transform
)
return ssl_dataset, eval_datasetIn this step, we load the CIFAR-10 dataset and apply separate transformations for self-supervised and evaluation phases. We create a custom SSLDataset class that generates multiple augmented views of each image for contrastive learning, while the evaluation dataset uses normalized images for downstream tasks. This setup helps the model learn robust representations invariant to visual changes. Check out the FULL CODES here.
def train_ssl_model(model, dataloader, epochs=5, device="cuda"):
"""Train SimCLR model"""
model.to(device)
criterion = NTXentLoss(temperature=0.5)
optimizer = torch.optim.SGD(model.parameters(), lr=0.06, momentum=0.9, weight_decay=5e-4)
print("\n=== Self-Supervised Training ===")
for epoch in range(epochs):
model.train()
total_loss = 0
for batch_idx, batch in enumerate(dataloader):
views = batch[0]
view1, view2 = views[0].to(device), views[1].to(device)
z1 = model(view1)
z2 = model(view2)
loss = criterion(z1, z2)
optimizer.zero_grad()
loss.backward()
optimizer.step()
total_loss += loss.item()
if batch_idx % 50 == 0:
print(f"Epoch {epoch+1}/{epochs} | Batch {batch_idx} | Loss: {loss.item():.4f}")
avg_loss = total_loss / len(dataloader)
print(f"Epoch {epoch+1} Complete | Avg Loss: {avg_loss:.4f}")
return modelHere, we train our SimCLR model in a self-supervised manner using the NT-Xent contrastive loss, which encourages similar representations for augmented views of the same image. We optimize the model with stochastic gradient descent (SGD) and track the loss across epochs to monitor learning progress. This stage teaches the model to extract meaningful visual features without relying on labeled data. Check out the FULL CODES here.
def generate_embeddings(model, dataset, device="cuda", batch_size=256):
"""Generate embeddings for the entire dataset"""
model.eval()
model.to(device)
dataloader = DataLoader(dataset, batch_size=batch_size, shuffle=False, num_workers=2)
embeddings = []
labels = []
print("\n=== Generating Embeddings ===")
with torch.no_grad():
for images, targets in dataloader:
images = images.to(device)
features = model.extract_features(images)
embeddings.append(features.cpu().numpy())
labels.append(targets.numpy())
embeddings = np.vstack(embeddings)
labels = np.concatenate(labels)
print(f"Generated {embeddings.shape[0]} embeddings with dimension {embeddings.shape[1]}")
return embeddings, labels
def visualize_embeddings(embeddings, labels, method='umap', n_samples=5000):
"""Visualize embeddings using UMAP or t-SNE"""
print(f"\n=== Visualizing Embeddings with {method.upper()} ===")
if len(embeddings) > n_samples:
indices = np.random.choice(len(embeddings), n_samples, replace=False)
embeddings = embeddings[indices]
labels = labels[indices]
if method == 'umap':
reducer = umap.UMAP(n_neighbors=15, min_dist=0.1, metric="cosine")
else:
reducer = TSNE(n_components=2, perplexity=30, metric="cosine")
embeddings_2d = reducer.fit_transform(embeddings)
plt.figure(figsize=(12, 10))
scatter = plt.scatter(embeddings_2d[:, 0], embeddings_2d[:, 1],
c=labels, cmap='tab10', s=5, alpha=0.6)
plt.colorbar(scatter)
plt.title(f'CIFAR-10 Embeddings ({method.upper()})')
plt.xlabel('Component 1')
plt.ylabel('Component 2')
plt.tight_layout()
plt.savefig(f'embeddings_{method}.png', dpi=150)
print(f"Saved visualization to embeddings_{method}.png")
plt.show()
def select_coreset(embeddings, labels, budget=1000, method='diversity'):
"""
Select a coreset using different strategies:
- diversity: Maximum diversity using k-center greedy
- balanced: Class-balanced selection
"""
print(f"\n=== Coreset Selection ({method}) ===")
if method == 'balanced':
selected_indices = []
n_classes = len(np.unique(labels))
per_class = budget // n_classes
for cls in range(n_classes):
cls_indices = np.where(labels == cls)[0]
selected = np.random.choice(cls_indices, min(per_class, len(cls_indices)), replace=False)
selected_indices.extend(selected)
return np.array(selected_indices)
elif method == 'diversity':
selected_indices = []
remaining_indices = set(range(len(embeddings)))
first_idx = np.random.randint(len(embeddings))
selected_indices.append(first_idx)
remaining_indices.remove(first_idx)
for _ in range(budget - 1):
if not remaining_indices:
break
remaining = list(remaining_indices)
selected_emb = embeddings[selected_indices]
remaining_emb = embeddings[remaining]
distances = np.min(
np.linalg.norm(remaining_emb[:, None] - selected_emb, axis=2), axis=1
)
max_dist_idx = np.argmax(distances)
selected_idx = remaining[max_dist_idx]
selected_indices.append(selected_idx)
remaining_indices.remove(selected_idx)
print(f"Selected {len(selected_indices)} samples")
return np.array(selected_indices)We extract high-quality feature embeddings from our trained backbone, cache them with labels, and project them to 2D using UMAP or t-SNE to visually see the cluster structure emerge. Next, we curate data using a coreset selector, either class-balanced or diversity-driven (k-center greedy), to prioritize the most informative, non-redundant samples for downstream training. This pipeline helps us both see what the model learns and select what matters most. Check out the FULL CODES here.
def evaluate_linear_probe(model, train_subset, test_dataset, device="cuda"):
"""Train linear classifier on frozen features"""
model.eval()
train_loader = DataLoader(train_subset, batch_size=128, shuffle=True, num_workers=2)
test_loader = DataLoader(test_dataset, batch_size=256, shuffle=False, num_workers=2)
classifier = nn.Linear(512, 10).to(device)
criterion = nn.CrossEntropyLoss()
optimizer = torch.optim.Adam(classifier.parameters(), lr=0.001)
for epoch in range(10):
classifier.train()
for images, targets in train_loader:
images, targets = images.to(device), targets.to(device)
with torch.no_grad():
features = model.extract_features(images)
outputs = classifier(features)
loss = criterion(outputs, targets)
optimizer.zero_grad()
loss.backward()
optimizer.step()
classifier.eval()
correct = 0
total = 0
with torch.no_grad():
for images, targets in test_loader:
images, targets = images.to(device), targets.to(device)
features = model.extract_features(images)
outputs = classifier(features)
_, predicted = outputs.max(1)
total += targets.size(0)
correct += predicted.eq(targets).sum().item()
accuracy = 100. * correct / total
return accuracy
def main():
device="cuda" if torch.cuda.is_available() else 'cpu'
print(f"Using device: {device}")
ssl_dataset, eval_dataset = load_dataset(train=True)
_, test_dataset = load_dataset(train=False)
ssl_subset = Subset(ssl_dataset, range(10000))
ssl_loader = DataLoader(ssl_subset, batch_size=128, shuffle=True, num_workers=2, drop_last=True)
backbone = torchvision.models.resnet18(pretrained=False)
model = SimCLRModel(backbone)
model = train_ssl_model(model, ssl_loader, epochs=5, device=device)
eval_subset = Subset(eval_dataset, range(10000))
embeddings, labels = generate_embeddings(model, eval_subset, device=device)
visualize_embeddings(embeddings, labels, method='umap')
coreset_indices = select_coreset(embeddings, labels, budget=1000, method='diversity')
coreset_subset = Subset(eval_dataset, coreset_indices)
print("\n=== Active Learning Evaluation ===")
coreset_acc = evaluate_linear_probe(model, coreset_subset, test_dataset, device=device)
print(f"Coreset Accuracy (1000 samples): {coreset_acc:.2f}%")
random_indices = np.random.choice(len(eval_subset), 1000, replace=False)
random_subset = Subset(eval_dataset, random_indices)
random_acc = evaluate_linear_probe(model, random_subset, test_dataset, device=device)
print(f"Random Accuracy (1000 samples): {random_acc:.2f}%")
print(f"\nCoreset improvement: +{coreset_acc - random_acc:.2f}%")
print("\n=== Tutorial Complete! ===")
print("Key takeaways:")
print("1. Self-supervised learning creates meaningful representations without labels")
print("2. Embeddings capture semantic similarity between images")
print("3. Smart data selection (coreset) outperforms random sampling")
print("4. Active learning reduces labeling costs while maintaining accuracy")
if __name__ == "__main__":
main()We freeze the backbone and train a lightweight linear probe to quantify how good our learned features are, then evaluate accuracy on the test set. In the main pipeline, we pretrain with SimCLR, generate embeddings, visualize them, pick a diverse coreset, and compare linear-probe performance against a random subset, thereby directly measuring the value of smart data curation.
In conclusion, we have seen how self-supervised learning enables representation learning without manual annotations and how coreset-based data selection enhances model generalization with fewer samples. By training a SimCLR model, generating embeddings, curating data, and evaluating through active learning, we experience the end-to-end process of modern self-supervised workflows. We conclude that by combining intelligent data curation with learned representations, we can build models that are both resource-efficient and performance-optimized, setting a strong foundation for scalable machine learning applications.
Check out the FULL CODES here. Feel free to check out our GitHub Page for Tutorials, Codes and Notebooks. Also, feel free to follow us on Twitter and don’t forget to join our 100k+ ML SubReddit and Subscribe to our Newsletter. Wait! are you on telegram? now you can join us on telegram as well.
Asif Razzaq is the CEO of Marktechpost Media Inc.. As a visionary entrepreneur and engineer, Asif is committed to harnessing the potential of Artificial Intelligence for social good. His most recent endeavor is the launch of an Artificial Intelligence Media Platform, Marktechpost, which stands out for its in-depth coverage of machine learning and deep learning news that is both technically sound and easily understandable by a wide audience. The platform boasts of over 2 million monthly views, illustrating its popularity among audiences.