In the pursuit of solutions to complex global challenges including disease, energy demands, and climate change, scientific researchers, including at MIT, have turned to artificial intelligence, and to quantitative analysis and modeling, to design and construct engineered cells with novel properties. The engineered cells can be programmed to become new therapeutics — battling, and perhaps eradicating, diseases.
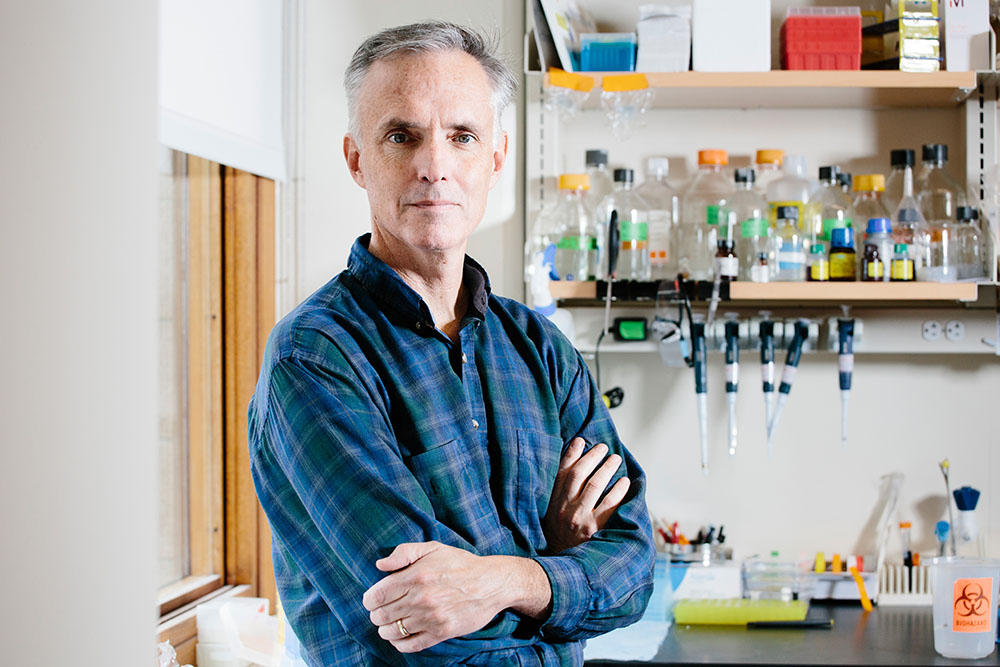
James J. Collins is one of the founders of the field of synthetic biology, and is also a leading researcher in systems biology, the interdisciplinary approach that uses mathematical analysis and modeling of complex systems to better understand biological systems. His research has led to the development of new classes of diagnostics and therapeutics, including in the detection and treatment of pathogens like Ebola, Zika, SARS-CoV-2, and antibiotic-resistant bacteria. Collins, the Termeer Professor of Medical Engineering and Science and professor of biological engineering at MIT, is a core faculty member of the Institute for Medical Engineering and Science (IMES), the director of the MIT Abdul Latif Jameel Clinic for Machine Learning in Health, as well as an institute member of the Broad Institute of MIT and Harvard, and core founding faculty at the Wyss Institute for Biologically Inspired Engineering, Harvard.
In this Q&A, Collins speaks about his latest work and goals for this research.
Q. You’re known for collaborating with colleagues across MIT, and at other institutions. How have these collaborations and affiliations helped you with your research?
A: Collaboration has been central to the work in my lab. At the MIT Jameel Clinic for Machine Learning in Health, I formed a collaboration with Regina Barzilay [the Delta Electronics Professor in the MIT Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science and affiliate faculty member at IMES] and Tommi Jaakkola [the Thomas Siebel Professor of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science and the Institute for Data, Systems, and Society] to use deep learning to discover new antibiotics. This effort combined our expertise in artificial intelligence, network biology, and systems microbiology, leading to the discovery of halicin, a potent new antibiotic effective against a broad range of multidrug-resistant bacterial pathogens. Our results were published in Cell in 2020 and showcased the power of bringing together complementary skill sets to tackle a global health challenge.
At the Wyss Institute, I’ve worked closely with Donald Ingber [the Judah Folkman Professor of Vascular Biology at Harvard Medical School and the Vascular Biology Program at Boston Children’s Hospital, and Hansjörg Wyss Professor of Biologically Inspired Engineering at Harvard], leveraging his organs-on-chips technology to test the efficacy of AI-discovered and AI-generated antibiotics. These platforms allow us to study how drugs behave in human tissue-like environments, complementing traditional animal experiments and providing a more nuanced view of their therapeutic potential.
The common thread across our many collaborations is the ability to combine computational predictions with cutting-edge experimental platforms, accelerating the path from ideas to validated new therapies.
Q. Your research has led to many advances in designing novel antibiotics, using generative AI and deep learning. Can you talk about some of the advances you’ve been a part of in the development of drugs that can battle multi-drug-resistant pathogens, and what you see on the horizon for breakthroughs in this arena?
A: In 2025, our lab published a study in Cell demonstrating how generative AI can be used to design completely new antibiotics from scratch. We used genetic algorithms and variational autoencoders to generate millions of candidate molecules, exploring both fragment-based designs and entirely unconstrained chemical space. After computational filtering, retrosynthetic modeling, and medicinal chemistry review, we synthesized 24 compounds and tested them experimentally. Seven showed selective antibacterial activity. One lead, NG1, was highly narrow-spectrum, eradicating multi-drug-resistant Neisseria gonorrhoeae, including strains resistant to first-line therapies, while sparing commensal species. Another, DN1, targeted methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) and cleared infections in mice through broad membrane disruption. Both were non-toxic and showed low rates of resistance.
Looking ahead, we are using deep learning to design antibiotics with drug-like properties that make them stronger candidates for clinical development. By integrating AI with high-throughput biological testing, we aim to accelerate the discovery and design of antibiotics that are novel, safe, and effective, ready for real-world therapeutic use. This approach could transform how we respond to drug-resistant bacterial pathogens, moving from a reactive to a proactive strategy in antibiotic development.
Q. You’re a co-founder of Phare Bio, a nonprofit organization that uses AI to discover new antibiotics, and the Collins Lab has helped to launch the Antibiotics-AI Project in collaboration with Phare Bio. Can you tell us more about what you hope to accomplish with these collaborations, and how they tie back to your research goals?
A: We founded Phare Bio as a nonprofit to take the most promising antibiotic candidates emerging from the Antibiotics-AI Project at MIT and advance them toward the clinic. The idea is to bridge the gap between discovery and development by collaborating with biotech companies, pharmaceutical partners, AI companies, philanthropies, other nonprofits, and even nation states. Akhila Kosaraju has been doing a brilliant job leading Phare Bio, coordinating these efforts and moving candidates forward efficiently.
Recently, we received a grant from ARPA-H to use generative AI to design 15 new antibiotics and develop them as pre-clinical candidates. This project builds directly on our lab’s research, combining computational design with experimental testing to create novel antibiotics that are ready for further development. By integrating generative AI, biology, and translational partnerships, we hope to create a pipeline that can respond more rapidly to the global threat of antibiotic resistance, ultimately delivering new therapies to patients who need them most.