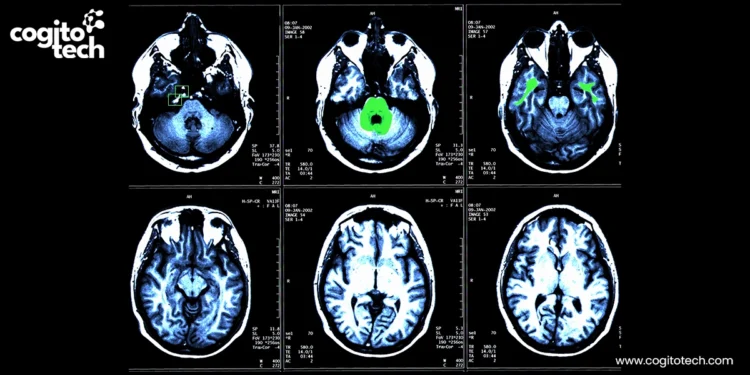
However, the ability of AI in the prevention and management of cardiovascular disease depends on the quality of cardiology datasets. Labeled data forms the backbone of imaging AI, shaping model performance, trustworthiness, and clinical applicability. High-quality labeled data enables AI models to deliver accurate diagnoses and reliable treatment recommendations.
This piece explores how cardiovascular imaging AI is developed and applied across clinical workflows, the critical role of data annotation in model development and deployment, and how Cogito Tech enables scalable, high-quality cardiovascular imaging AI through expert-led annotation and compliance-ready processes.
Why data annotation matters for cardiovascular image labeling
Accurately labeled data is essential for developing cardiovascular AI models, particularly as cardiology increasingly relies on advanced medical imaging not only for diagnosis but also to guide interventions and determine prognosis. Model performance depends on large volumes of labeled data to learn and recognize patterns associated with specific cardiac conditions. As imaging-based and explainable AI models must be both accurate and interpretable, labeling errors – such as fuzzy contours, sparse lesion markings, and a lack of heterogeneous datasets – can lead to bias, poor generalization, missed diagnostic signals, and incorrect treatment recommendations.
Annotation of cardiovascular data, including ECG waveforms, cardiac imaging structures, and cardiac events, enables the extraction of precise and interpretable information required to train, validate, and deploy reliable AI models in real-world clinical settings.
Types of cardiovascular imaging data annotation
Cardiac imaging annotation
- CT (CCTA): In coronary CT angiography (CCTA), annotations capture coronary arteries, cardiac chambers, valve leaflets, and calcific plaques, enabling automated stenosis detection and Agatston calcium scoring.
- Cardiac MRI: This involves segmenting the ventricles, atria, myocardium, and pericardial fat, as well as labeling tissue characteristics such as late gadolinium enhancement (LGE) scars. These annotations help AI models analyze cardiac function, fibrosis, and metabolic risk.
- Echocardiography: Both adult and fetal echocardiography studies are annotated by delineating valve leaflets, chamber boundaries, and Doppler flow regions to support ejection fraction calculation and congenital heart disease assessment.
- ECGI: This involves labeling hear-signal data to show activation times, recovery patterns, and hotspots of unstable or abnormal electrical activity. These annotations enable AI systems to pinpoint the exact sources of arrhythmias, such as atrial fibrillation or ventricular tachycardia, guiding targeted ablation procedures.
Vascular imaging annotation
Arteries
- Intracranial imaging: The circle of Willis is segmented on CT and MR angiograms, with aneurysms, hemorrhages, and occlusions labeled to enable cerebrovascular risk analysis.
- Carotid arteries: Annotation on CT and Doppler ultrasound includes measurements of intima–media thickness, identification of calcified plaques, and assessment of flow characteristics to support stroke risk prediction and atherosclerosis monitoring.
- Aorta (Full Length): Across the full length of the aorta—from the root to the bifurcation—annotations identify the lumen, thrombi, aneurysms, dissections, and post-intervention endografts on CTA datasets.
- Peripheral arteries: IVUS and CT studies of limb and renal arteries are annotated to map plaques, stenoses, and occlusions relevant to peripheral artery disease (PAD) diagnosis and management.
Veins
- Limb veins: IVUS and duplex ultrasound datasets are annotated to segment thrombi, venous walls, and flow disruptions, supporting AI-based detection of deep vein thrombosis (DVT) and chronic venous insufficiency.
Data annotation for interventional cardiology systems
Beyond diagnostic imaging, cardiovascular AI development relies on precise data annotation of procedural, imaging, and clinical datasets used throughout interventional cardiology workflows. This includes detailed vessel and lesion labeling in coronary angiograms, catheter and stent segmentation in procedural videos, and structured coding of diagnoses, procedures, and outcomes from EHRs.
These annotations enable AI systems to support automated angiogram interpretation, real-time device guidance, high-risk plaque detection, cardiac function and valve assessment, procedure phase recognition, and accurate risk and outcome prediction – ensuring reliable, explainable, and clinically usable interventional cardiology solutions.
AI and annotated cardiovascular imaging in interventional cardiology
Doctors rely on noninvasive cardiovascular imaging to plan and guide catheter-based heart procedures. Imaging methods, such as echocardiography and MRI for structural and functional assessment, nuclear imaging for perfusion, and CT scans for detailed anatomical visualization, offer complementary insights for diagnosis and outcome prediction.
While using multimodality imaging is critical for guiding minimally invasive procedures, the increasing complexity and volume of imaging data make interpretation challenging. AI, especially deep learning, helps address these challenges by processing and analyzing large numbers of images, detecting subtle patterns that humans may miss, and reducing inter-reader variability and diagnostic errors.
The following sections highlight how AI-enhanced imaging outputs improve interventional cardiology workflows, clinical decision-making, and patient outcomes.
Coronary artery interventions
Percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI) increasingly relies on AI-ready imaging data derived from noninvasive modalities such as CCTA. Annotated images of coronary arteries, stenotic segments, and perfusion features enable AI models to noninvasively estimate fractional flow reserve (FFR) through 3D reconstruction of vascular anatomy.
These annotated datasets support accurate detection and grading of coronary stenosis, delivering rapid assessments that can inform preprocedural planning without invasive testing. Preinterventional CCTA annotation also supports workflow optimization by guiding vascular access selection, fluoroscopy angle planning, and procedural strategy development, helping reduce procedural complexity and risk.
Large-scale, consistently labeled imaging and clinical datasets further allow ML systems to identify patients most likely to benefit from intervention, supporting data-driven patient selection and personalized treatment planning in interventional cardiology.
Structural heart transcatheter interventions

Modern heart surgery is increasingly shifting from a manual approach to an AI-driven, “precision” approach. AI-enabled workflows developed using high-quality cardiac MRI, CT, and echocardiography data enable automated functional assessments and accurate valvular measurements, while significantly reducing analysis time. Consistent annotation of valvular anatomy and surrounding cardiac structures supports faster, more reliable preoperative and perioperative planning.
Machine learning models trained on annotated transesophageal echocardiography (TEE), CTA, and MRI datasets enable patient-specific simulation of valve anatomy and device deployment. These capabilities help clinicians select optimal devices, determine appropriate implantation depth, and refine procedural strategies for improved outcomes.
Electrophysiological cardiac interventions
Electrophysiological cardiac interventions focus on treating cardiac arrhythmias, such as atrial fibrillation and ventricular tachycardia, using catheter ablation, a minimally invasive heart procedure. Traditionally, identifying the arrhythmogenic focus involved significant trial and error. Today, AI can analyze MRI data and identify scar tissue (the “myocardial scar”) and generate precise maps, enabling clinicians to accurately target ablation sites.
Structured labeling of cardiac MRI and late gadolinium enhancement (LGE) images – covering myocardial tissue properties, scar regions, and key anatomical landmarks – supports deep learning models for automated scar quantification, arrhythmia focus localization, and ablation strategy planning. These annotations also enable real-time guidance systems and robotic-assisted interventions by improving anatomical mapping and reducing fluoroscopy exposure. High-quality, clinically validated annotations are critical for training scalable and reliable AI models in electrophysiology imaging applications.
How Cogito Tech’s CCTA reader-led training data supports cardiovascular AI
Cogito Tech’s Medical AI Innovation Hubs integrates board-certified CCTA readers – including Level 1, Level 2, and Level 3 qualified cardiologists, cardiac radiologists, and other cardiovascular imaging specialists to deliver HIPAA-compliant, clinically vetted labels. These expert-led labeling workflows accelerate cardiovascular AI development while ensuring diagnostic accuracy and clinical relevance.
- Specialist-led annotation: Our medical hubs provide labels drawn under the guidance of board-certified professionals – including vessel contours, myocardial and chamber boundaries, plaques, and lesions – that serve as reliable ground truth for training high-performance AI models.
- Multi-modality diversity: By curating large, expertly annotated datasets across echocardiography, CT, MRI, and PET/SPECT imaging, our teams capture variations in anatomy, pathology, scanner types, and acquisition protocols. This diversity is essential for building robust and generalizable cardiovascular imaging AI systems.
- Explainability by design: Annotations are created with downstream explainable AI (XAI) requirements in mind. Each segmentation aligns with clinical reasoning, helping models remain transparent, interpretable, and aligned with FDA expectations.
- Audit-ready, compliant workflows: Cogito Tech’s proprietary DataSum framework provides “nutrition label”–style transparency for every dataset. Combined with 21 CFR Part 11–aligned processes, this enables smoother regulatory pathways, including FDA 510(k) submissions and CE marking.
Conclusion
As cardiovascular care increasingly shifts toward data-driven, minimally invasive, and precision-based interventions, the effectiveness of AI systems hinges on the quality, consistency, and clinical relevance of annotated imaging data. From noninvasive diagnostics and interventional planning to electrophysiology and structural heart procedures, high-quality training data ensures that AI models are not only accurate but also explainable, generalizable, and clinically trustworthy.
By combining specialist-led annotation, multi-modality expertise, and compliance-ready workflows, Cogito Tech enables cardiovascular AI developers to progress from model development to clinical deployment. In an era where regulatory scrutiny and clinical accountability are instrumental, robust data annotation is no longer optional – it is foundational to building safe, scalable, and impactful cardiovascular imaging AI solutions.